Younger cheerleaders threat accidents as they tackle bold stunts : Photographs
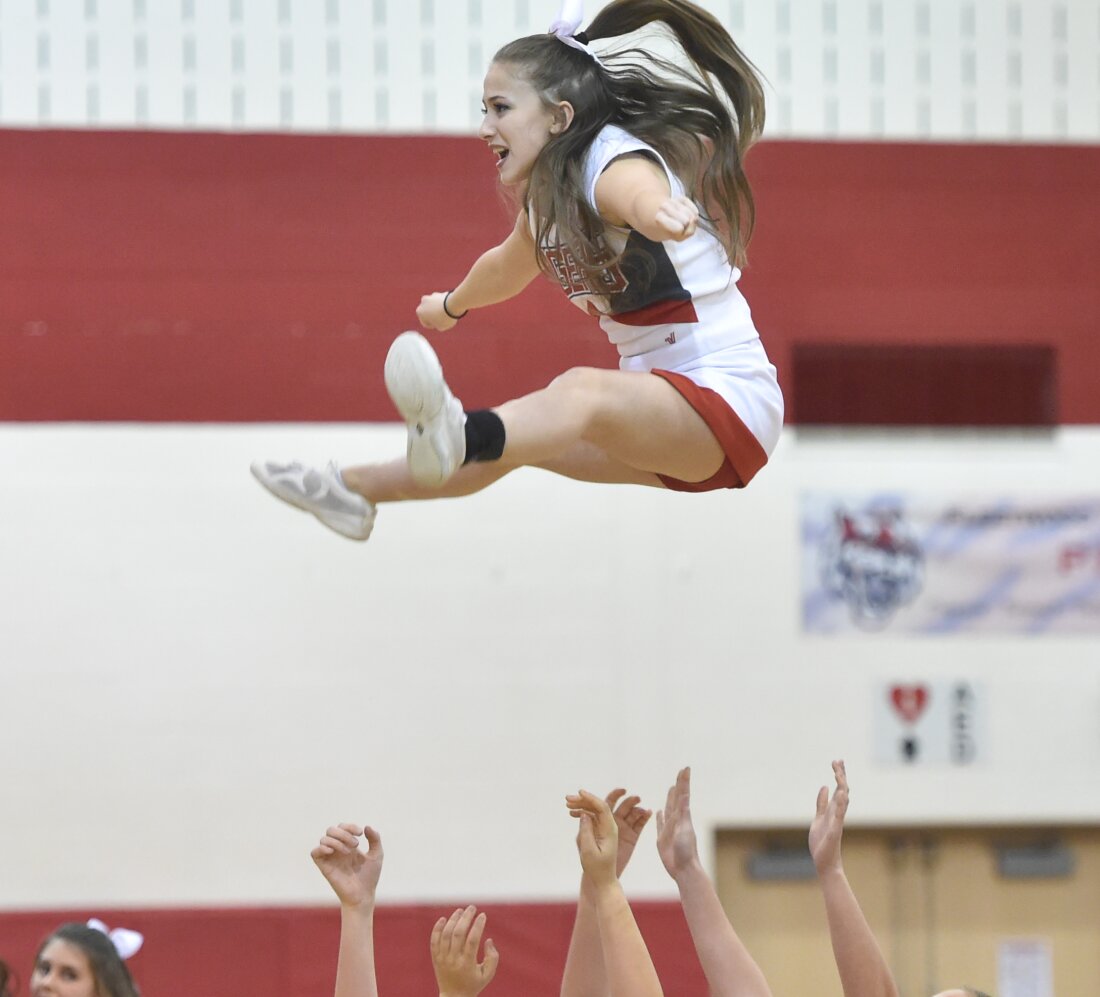
Fleetwood Excessive College cheerleader Samantha Colelli, 17, a senior at Fleetwood, does a basket throughout halftime at a recreation in 2017. As cheerleading has change into extra bold during the last decade, it is also change into riskier warn pediatricians.
Harold Hoch/MediaNews Group/Studying Eagle/Getty Photographs
cover caption
toggle caption
Harold Hoch/MediaNews Group/Studying Eagle/Getty Photographs
Dr. Amy Xu acquired hooked on cheerleading within the fifth grade.
As she pursued the game in highschool and faculty, she witnessed how the routines began demanding more and more complicated acrobatic feats — tall human towers and tumbling passes with many twists and flips.
It wasn’t uncommon for her and her teammates to get concussions and different accidents.
“I noticed people which can be continually battling by way of power circumstances, struggling by way of acute accidents as a result of it is a sport that requires follow and participation all yr lengthy,” says Xu, now an orthopedic resident on the Hospital for Particular Surgical procedure in New York.
Xu, who has printed analysis on accidents associated to cheerleading, says the game that isn’t actually talked about a lot within the literature.
Pediatricians at the moment are elevating consciousness of the dangers. For the primary time in over a decade the American Academy of Pediatrics has issued an up to date assertion this week on the dangers of accidents associated to youth cheerleading, and easy methods to forestall them.
The group is looking for cheerleading to be formally acknowledged as a sport, and for cheerleaders to get the identical sources and help as different athletes.
Dr. Gregory Canty, who co-authored the AAP assertion, says he sees cheerleading sufferers “day by day” in his medical follow.
“Because the athleticism and the peak on [cheerleading] stunts get greater and better, that results in an elevated threat of damage — and some extent of significant damage,” says Canty, medical director on the Sports activities Drugs Middle at Youngsters’s Mercy hospital in Kansas Metropolis, Mo.
A younger cheerleader takes a photograph of her teammates practising in the course of the Frost Excessive cheerleading occasion in Wilmington, Delaware, on January 29, 2023. Nearly all of cheerleaders are ladies aged 6-17.
Andrew Caballero-Reynolds/AFP/Getty Photographs
cover caption
toggle caption
Andrew Caballero-Reynolds/AFP/Getty Photographs
And whereas the general charge of damage in cheerleading is 2 to a few instances decrease than ladies’ soccer or ladies’ basketball, cheerleading accidents, notably concussions, “might be extreme and so they can have extended restoration time,” Canty says.
Cheerleading has gotten extra athletic and extra harmful through the years.
Again within the 1800’s, males led cheers on the sidelines at video games. Now, the overwhelming majority of the three.5 million U.S. youth in cheerleading are ladies between the ages of 6-17. And the game has developed from clapping and waving on the sidelines into intricate multi-person routines, or stunts, that contain leaping, tumbling and tossing athletes within the air.
USA Cheer, a sports activities governing physique, describes “stunt” cheerleading as “one of many quickest rising feminine sports activities within the nation.”
Stunting can also be implicated in almost 70% of the concussions reported in highschool cheerleading, in keeping with information included within the AAP report. “The concussion threat has gone up fairly a bit” previously ten years, says Canty, including that concussion diagnoses and reporting have additionally improved in that point.
“I see fairly a number of cheerleaders for persistent post-concussion signs,” says pediatric neurologist Dr. Brittany Poinson at Youngsters’s Hospital New Orleans, who wasn’t concerned within the new AAP report. “Lots of households who’ve youngsters concerned in cheer don’t acknowledge the dangers, nevertheless it positively happens.”
The chance of damage runs excessive even throughout follow.
Cheerleading’s concussion charge throughout follow ranks third behind boys’ soccer and boys’ wrestling practices, in keeping with the AAP report. “Which will correlate with the truth that they’re nonetheless buying the abilities and so they’re attempting to be taught the right strategies to guard themselves,” Poinson says.
Accidents in cheerleading usually occur when athletes doing multi-person aerial stunts collide with one another or the bottom. Coverage adjustments have already made some stunts safer.
In 2006, governing our bodies for the game started prohibiting the “basket toss” – when a cheerleader is launched into the air by a workforce of individuals whose arms are interlocked – on laborious floor. Analysis reveals that requiring the “basket toss” to be carried out on absorbent surfaces corresponding to grass or rubber mats lower catastrophic accidents associated to the transfer by almost 75% within the following decade.
“What that highlights for me is that if we check out the place and when these accidents occur, it could possibly result in actual adjustments that proceed to make the game safer whereas maintaining it thrilling for individuals,” Canty says.
Regardless of the game’s recognition, the Nationwide Collegiate Athletics Affiliation and lots of state highschool sports activities associations don’t acknowledge it as an official sport. That makes it laborious to gather complete information on accidents and in the end enhance the security of the game, says Canty.
Formal recognition would additionally enhance entry to certified coaches, coaching amenities and damage care, in accordance the AAP coverage assertion.
“There are accidents [in cheerleading] which can be extreme and frequent, and [cheer teams] needs to be given entry to the identical sources as different athletic groups like soccer and soccer,” says Xu.
In its coverage assertion, the AAP additionally requires bodily well being screenings for potential athletes and emergency motion plans which can be posted prominently in coaching amenities.


